

30 Oct Matte painting- modern technologies-ARD 516
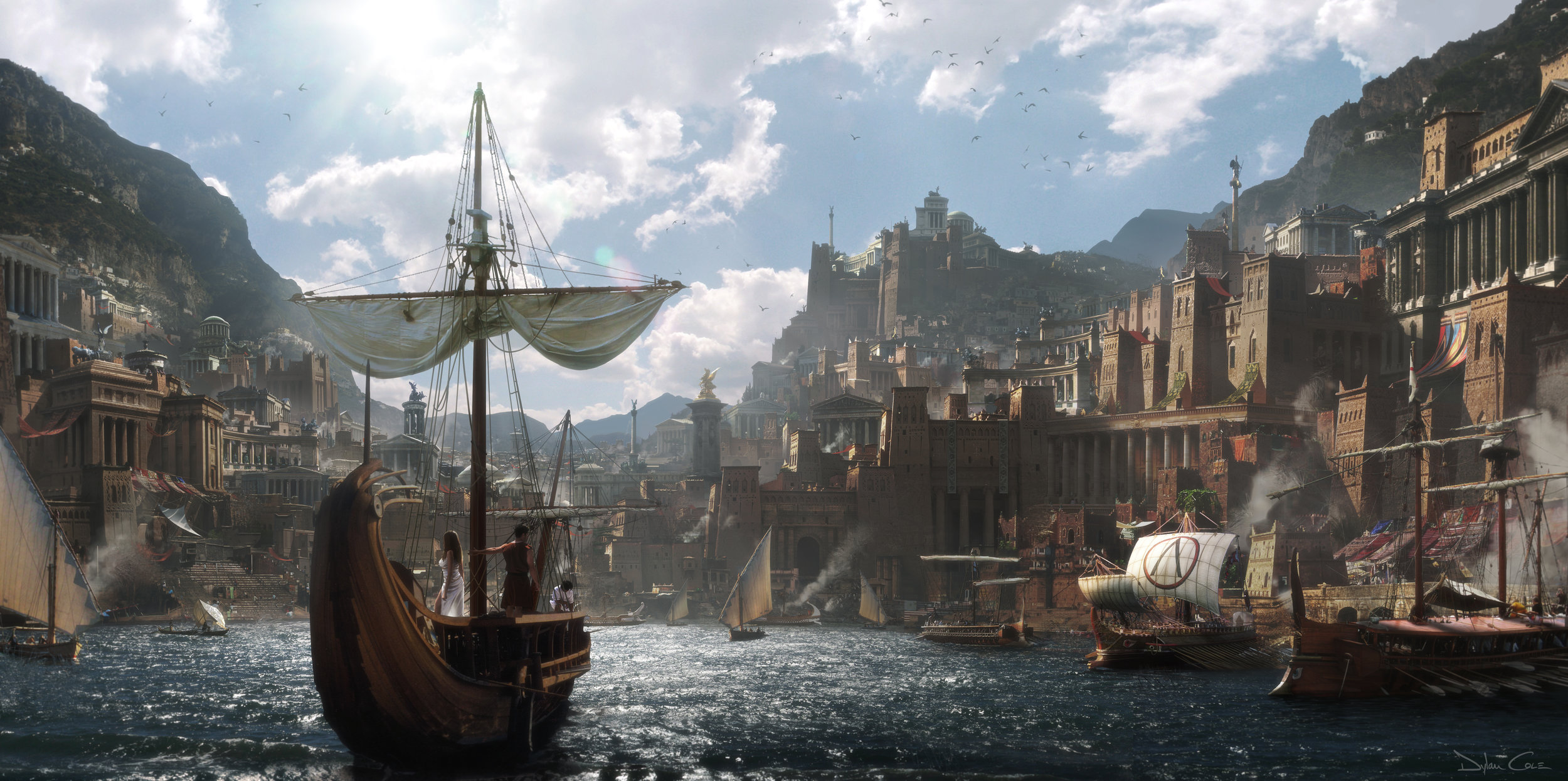
Throughout the 1990s, traditional matte paintings were still in use, but more often in conjunction with digital compositing. Die Hard 2 (1990) was the first film to use digitally composited live-action footage with a traditional glass matte painting that had been photographed and scanned into a computer. It was for the last scene, which took place on an airport runway. By the end of the decade, the time of hand-painted matte paintings was drawing to a close, although as late as 1997 some traditional paintings were still being made, notably Chris Evans’ painting of the RMS Carpathia rescue ship in James Cameron’s Titanic.
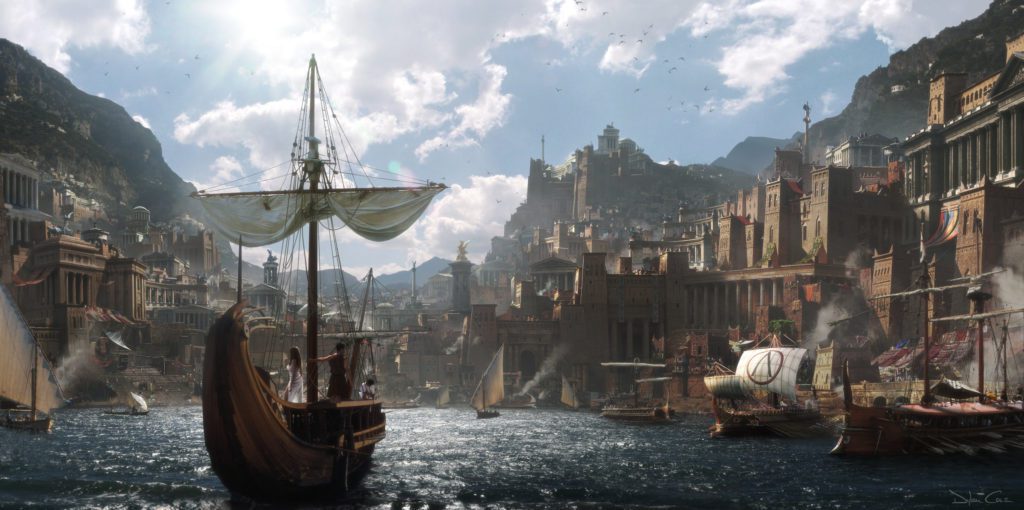


Paint has now been superseded by digital images created using photo references, 3-D models, and drawing tablets. Matte painters combine their digitally matte painted textures within computer-generated 3-D environments, allowing for 3-D camera movement. Lighting algorithms used to simulate lighting sources expanded in scope in 1995, when radiosity rendering was applied to film for the first time in Martin Scorsese’s Casino. Matte World Digital collaborated with LightScape to simulate the indirect bounce-light effect of millions of neon lights of the 70s-era Las Vegas strip. Lower computer processing times continue to alter and expand matte painting technologies and techniques. Matte painting techniques are also implemented in concept art and used often in games and even high end production techniques in animation in today’s society.

Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.